Đề Kiểm Tra
Tìm giới hạn $\underset{x\to +\infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{2x-3}{1-3x}$ :
Kết quả của giới hạn $\underset{x\to 2}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{{{x}^{2}}-4}{x-2}$ bằng:
Tìm
tất cả các giá trị của m để hàm số 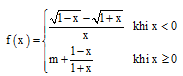 liên tục tại
$x=0.$
liên tục tại
$x=0.$
Tính $I=\underset{x\to 1}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{2x-\sqrt{x+3}}{{{x}^{2}}-1}$ ?
Tính giới hạn \[\underset{x\to {{1}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{2x+1}{x-1}.\]
Giới hạn \[\underset{x\to -\infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{x-\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+x}}{x+1}\] bằng
Tính $I=\lim \frac{2n-3}{2{{n}^{2}}+3n+1}.$
Tìm $\underset{x\to 1}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{\sqrt{x+3}-2}{x-1}$ .
Cho hàm số .png) liên tục tại \[x=2.\,\] Tính \[I=a+b?\]
liên tục tại \[x=2.\,\] Tính \[I=a+b?\]
Tìm giới hạn \[\underset{x\to 0}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{{{\left( 1+2x \right)}^{2}}-1}{x}.\]
Tính giới hạn $L=\underset{x\to 3}{\mathop{\lim
}}\,\frac{x-3}{x+3}$ .
Cho giới hạn $I=\lim \frac{\sqrt{4{{n}^{2}}+5}+n}{4n-\sqrt{{{n}^{2}}+1}}.$ Khi đó, giá trị của I là:
Giá trị của $\lim \frac{2-n}{n+1}$ bằng:
Tìm tất cả các giá trị thực của m để hàm số .png) liên tục trên R.
liên tục trên R.
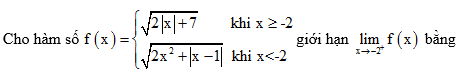
| 1 |
carddienthoai
trần bá kiệt
|
4/15
|
Đề Kiểm Tra
-
Bạn đồng ý:
- Làm đề thi trắc nghiệm nghiêm túc
- Đã đọc tên đề thi trước khi làm